In November 1993, the Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act (Brady Act) was signed into law. The Brady Act requires Federal Firearms Licensees (FFLs) to request background checks on individuals attempting to receive a firearm. The permanent provisions of the Brady Act, which went into effect on November 30, 1998, required the United States Attorney General to establish the National Instant Criminal Background Check System (NICS) so that any FFL may contact for information to be supplied immediately as to whether the receipt of a firearm by a prospective transferee would violate Title 18, United States Code (U.S.C.), Section 922 (g) or (n) or state law.
The NICS Section, located at the FBI's Criminal Justice Information Services Division in Clarksburg, West Virginia, provides full service to FFLs in 30 states and five U.S. territories, and the District of Columbia. Upon completion of the required Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) Form 4473, FFLs contact the FBI NICS Section, via a toll-free telephone number or electronically through the NICS E-Check System via the Internet, to request a background check with the descriptive information provided on the ATF Form 4473. The NICS is customarily available 17 hours a day, 7 days a week, including holidays (except for Christmas).
Thirteen states have agencies acting on behalf of the NICS in a full Point-Of-Contact (POC) capacity. These POC states, which have agreed to implement and maintain their own Brady NICS Program, conduct firearm background checks for FFLs' transactions in their respective states by electronically accessing the NICS. Upon completion of the required ATF Form 4473, the FFLs conducting business in the POC states contact a designated state agency to initiate a NICS background check in lieu of contacting the NICS Section.
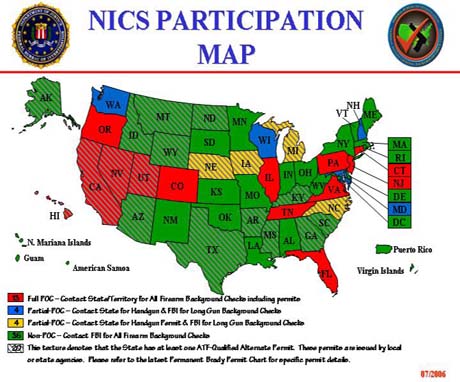
Additionally, eight states are currently sharing responsibility with the NICS Section by acting as partial POCs. Partial-POC states have agencies designated to conduct checks for handguns and/or handgun permits, while the NICS Section handles the processing of the states transactions for long gun purchases. The NICS Participation Map, as illustrated below, depicts each state's level of participation with the NICS.
Record information that would exhibit and/or clarify an individuals prohibitive status pursuant to the Brady Act is vital to the NICS in order to determine subject eligibility to receive and/or possess a firearm. Records contained within the databases searched by the NICS include those of the Interstate Identification Index (e.g., millions of criminal history records), the National Crime Information Center (e.g., protection orders and active felony or misdemeanor warrants) and the NICS Index, a database created solely for the use of the NICS which contains information provided by local, state and federal agencies pertaining to persons prohibited under federal law from receiving or possessing a firearm. Additionally, a fourth search of the applicable databases via the Department of Homeland Security's United States Immigration and Customs Enforcement will be conducted for background checks initiated on all non-United States citizens.
The federally prohibitive criteria outlining the reasons an individual may be precluded from the transfer/possession of a firearm or firearm-related permit, pursuant to Title 18 U.S.C., �� 922 (g) and (n), are as follows:
-
A person convicted in any court of a crime punishable by imprisonment for a term exceeding one year, whether or not sentence is imposed. This includes misdemeanor offenses with a potential term of imprisonment in excess of two years, whether or not sentence was imposed.
-
Persons who are fugitives of justice; for example, the subject of an active felony or misdemeanor warrant.
-
An unlawful user and/or an addict of any controlled substance; for example, a person convicted for the use or possession of a controlled substance within the past year, or a person with multiple arrests for the use or possession of a controlled substance within the past five years with the most recent arrest occurring within the past year, or a person found through a drug test to use a controlled substance unlawfully, provided the test was administered within the past year.
-
A person adjudicated mental defective or involuntarily committed to a mental institution or incompetent to handle own affairs, including dispositions to criminal charges pertaining to found not guilty by reason of insanity or found incompetent to stand trial.
-
An alien illegally/unlawfully in the United States or a non-immigrant who does not qualify for the exceptions under Title 18 U.S.C. Section 922(y); for example, not have possession of a valid hunting license.
-
A person dishonorably discharged from the United States Armed Forces.
-
A person who has renounced his/her United States citizenship.
-
The subject of a protective order issued after a hearing in which the respondent had notice that restrains them from harassing, stalking, or threatening an intimate partner or child of such partner. This does not include ex parte orders.
-
A person convicted in any court of a misdemeanor crime which includes the use or attempted use of physical force or threatened use of a deadly weapon and the defendant was the spouse, former spouse, parent, guardian of the victim, by a person with whom the victim shares a child in common, by a person who is cohabiting with or has cohabited in the past with the victim as a spouse, parent, guardian or similarly situated to a spouse, parent or guardian of the victim.
-
� A person under indictment or information for a crime punishable by imprisonment for a term exceeding one year.



